While the residential storage market has been slower to take off, a number of factors suggest that consumers may be willing to include batteries in addition to their PV systems.
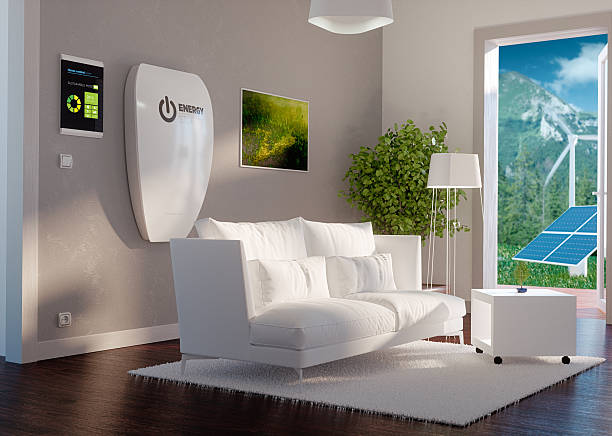

While the residential storage market has been slower to take off, a number of factors suggest that consumers may be willing to include batteries in addition to their PV systems.
As grid constraints, public safety power outages, fires, and other natural disasters become more common, homeowners suffer the painful, inconvenient consequences. Simultaneously, as the cost of fossil fuel power continues to rise, recent net-metering policy changes provide lower credits for selling surplus solar back to the grid and incentivize homes to store excess power in batteries. Other cities experiencing grid instability may follow suit soon.
Manufacturers have created some exciting solutions as technology has continued to evolve. Previously, users had to choose between powering critical and non-critical loads with partial home battery backup; however, it is now possible to have a solar-backed storage solution that can hold enough power to run a home's air conditioning, major appliances, and charge an EV while keeping the lights on. It doesn't have to be more expensive than powering critical loads, thanks to product advancement and generous government incentives. The benefits of on-demand power, storm protection, lower utility bills, and full-home energy management with minimal maintenance and intelligent integration are augmented by quick configuration and flexible features. Installers are embracing these new all-in-one systems due to their flexibility, intelligence, and low crew requirements for installation, setup, and support.
Closing the education gap
Whole-home storage has a two-fold market potential, with viability for first-time residential solar projects as well as retrofits of existing PV systems. The main barrier to widespread residential storage is the same as it was for selling home solar: education. Again, installers will be primarily responsible for interacting with current and potential customers. Solar power providers can assist clients by providing product information and emphasizing the benefits of resiliency, cost, and scalability in meeting future energy needs.
Here are some key points for installers to remember when assisting homeowners in understanding how whole-home residential storage options can benefit them while also considering a smooth implementation and maintenance experience for satisfied customers.
Full home vs. critical load
Traditional residential energy storage technology can only provide enough electricity to power necessities like heating, lighting, refrigeration, and outlets for small appliances and charging devices.
Full-home backup: Including enough electricity storage to power the entire house eliminates the need for homeowners to select which loads will be available during an outage. Whole-house load management encompasses both critical and non-critical loads such as air conditioning, water heaters, laundry, ovens, and stoves.
Important factors for homeowners and installers to consider when deciding between partial vs. full-home backup include:
Residential energy storage is inexpensive because it is modular. To accommodate more loads, homeowners can add more battery modules or units. Installers can assist homeowners in determining how many units are required to provide partial or complete home backup and how this affects cost. It's natural to assume that whole-home load management systems would be significantly more expensive due to the need for multiple inverters, larger batteries, and longer installation times. Residential energy storage systems, on the other hand, offer slim, stackable battery modules, DC-coupled hybrid inverters, and turnkey systems with increased intelligence and maximum storage capacity. The ability to power partial or full-home backup appeals to homeowners because it allows them to maximize efficiency and validate their investment. Installing energy storage solutions in smaller increments enables them to rightsize their home, customize capacity, and optimize usage and consumption, resulting in significant long-term cost savings.
Installation: Previous non-partial home power products were difficult to configure and expensive to maintain, but technological advances have reduced wiring complexity, made modules lighter, and made installation and configuration faster. Distributors can help by assisting installers in understanding the complexities of new systems, allowing installers to help homeowners weigh the pros and cons of adding different-sized units for the best long-term fit.
Space and aesthetics: While homeowners may recall bulky, unsightly storage units from the past, they can now enjoy sleek, stackable models that take up much less space. Many energy storage companies provide slim weather-resistant units that can be housed indoors or outdoors and can be wall-mounted or placed at ground level.
Performance:Manufacturers implement these safeguards to ensure that battery modules effectively prevent thermal runaway and provide overall performance, chemical stability, and a longer service life. Installers value simplicity and speed when it comes to serving a customer. The advancements in these whole-home solutions enable installers to work more efficiently and expand their services by providing dependable, high-performance products that require minimal maintenance and support.
The future of energy independence
It's also worth noting that homeowners are hearing critics and skeptics of clean energy initiatives downplay the increase in residential solar and storage and deny that these solutions are globally sustainable for future generations. With so much ambiguity and conflicting information, consumers are turning to industry experts for guidance. It is the installer's responsibility to assist homeowners in selecting the smartest solution to ensure their needs are met and their investment generates a return.
Understanding the benefits and specifics of installing a full-home backup system is critical to assisting consumers in feeling confident that they are making sound decisions for their homes and the environment. Homeowners can also feel good about lowering their carbon footprint by using more clean energy. Residential solar combined with storage investments can significantly reduce carbon pollution.
Energy storage continues to evolve, with new solutions being introduced on a daily basis that feature sleek design, quick configuration, and built-in intelligence. Leading global energy providers must meet the increasing demand for residential solar with a vision of instilling energy independence, a simple installation process, and homeowner relief. The ability to power an entire house at a low cost is an exciting step toward residential energy independence and, thus, combating the effects of climate change. We should see significant market growth in 2023 with increased consumer education.

B2U Storage Solutions, which repurposes electric vehicle batteries for energy storage systems, has begun operations at its SEPV Sierra hybrid solar + storage facility in Lancaster, California, with a 25-MWh system. The storage capacity of the project is m
While the residential storage market has been slower to take off, a number of factors suggest that consumers may be willing to include batteries in addition to their PV systems.